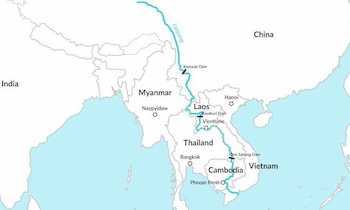
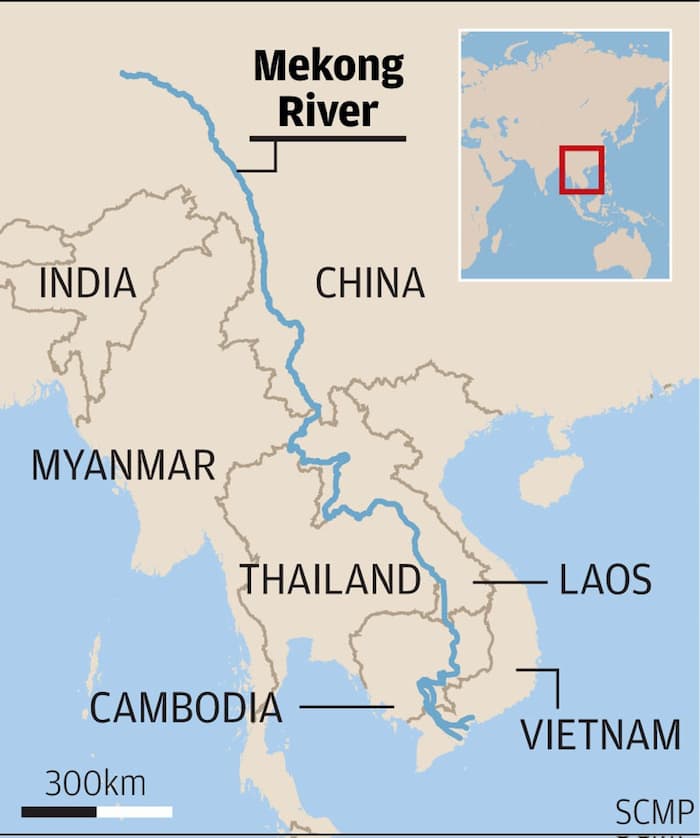
Where is the Mekong River location on the world map?
As one of the largest rivers in the world, the Mekong River carries a lush and luxuriant beauty. Besides, it also creates a unique culture for the places where it flows through, attracting many tourists to explore.
So, what do you know about the Mekong River? Where is the Mekong River location on the world map?
If you have ever learned about this famous tourist destination, you can imagine life and activities here. However, documents for tourists often do not fully comprise enough information.
Therefore, we will provide you everything about the Mekong River, from “where is the Mekong River located?”, area, flow to its attractions, unique activities, etc.
If you want to travel to a completely colorful and lively world, don't miss this article.
Geographical location
Where is the Mekong?
The Mekong is a wide delta region located in Asia. The Mekong River is one of the largest rivers in the world.
Where does the Mekong River start?
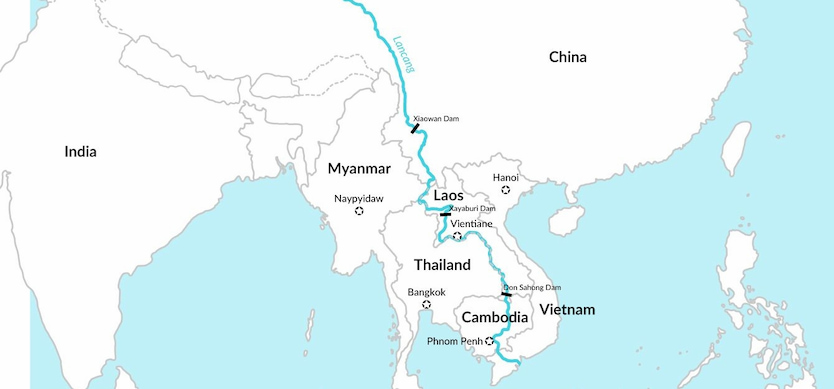
The Mekong River flows through six Asian countries
This river comes from the high mountains of Qinghai province, passing through Tibet along the length of Yunnan province (China), through Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, and Cambodia before entering Vietnam.
How long is the Mekong River?
In terms of length, the Mekong River is ranked 12th (7th in Asia). Also, when it comes to water flow, it ranks 10th in the world. Its basin is about 800,000 km² wide.
An outstanding hydrodynamic characteristic of the Mekong River is the role of water flow regulation by Tonlé Sap Lake - Southeast Asia's largest freshwater lake.
Flow
Tibetans believe that upstream of the Mekong River split into two branches, including the northwestern branch (Dzanak Chu) and the northern branch (Dzakar Chu). The northwest one is near Lungmug Pass with a length of 87.75 km, containing two sub-branches with a length of 91.12 km and 89.76 km.
The watershed of the river has now been clearly identified that belongs to the northern branch through recent expeditions of China, Japan, France, and the United States. The length of the river ranges from 4,200 km to 4,850 km.
Nearly half of this river flows on Chinese territory. Most of its section has deep gorges. Leaving Chinese territory, the river is only about 500 m above sea level.
After that, a section which is about 200 km long forms the border between the two countries of Myanmar and Laos. At the end of the border, the river joins the Ruak River in the Golden Triangle. This place is also the dividing point for Upper and Lower parts of the Mekong River.
The Mekong River then forms the border of Laos and Thailand before flowing into Laos in Bokeo province. The river in Laos is characterized by deep gorges, fast currents, and shallow pools of water which are about half a meter deep in the dry season.
The river then forms the border of Laos and Thailand in the section flowing through Vientiane to Champasak province. The next is a short part in Laos with a tributary on the left bank that is Xe Don river flowing into Pak Se.
In Cambodia, this river is called the Mekong River or Tong-Le Thom River. The area of Stung Treng town is where the Tonle San river flows into. Above Phnom Penh, it merges with Tonle Sap, its main tributary in Cambodia.
From Phnom Penh, it divides into two branches. Of which, the right is Ba Thac River (or Hau River in Vietnam), and the left is Mekong River (or Tien River in Vietnam). Both flow into the vast delta region of South Vietnam, about 220–250 km long.

The Hau River in Vietnam
The group of all nine major river branches in Vietnam is collectively referred to as the Mekong Delta or Cuu Long River (Nine-Dragon River).
The tributaries
-
Ruak River originates from Shan State, Myanmar, flows to the Golden Triangle and has a river door that is also the border of Myanmar - Thailand.
-
Nam Ou originates from Yunnan, China, flowing by Phongsaly province into the Mekong River at Muang Pak Ou. There is a small upstream tributary, Nam Nua, originating in Nua Ngam commune, Dien Bien province, Vietnam. When it comes to Laos, it is called Nam Neua. It flows into Nam Ou in Muang Khua.
-
Nam Ngum, 354 km long, originates from the mountainous area north of Xiengkhouang province and flows south through Vientiane province into the Mekong River in the south of Vientiane city.
-
Nam Theun originates from Truong Son range on the Laos-Vietnam border in Khammouane province, flowing into the Mekong in Pak Kading district of Bolikhamxay province.
-
Se Bangfai originates from the Truong Son range, Boualapha district of Khammouane Province and flows into the Mekong River on the border of Savannakhet and Khammouan provinces.
-
Se Banghiang originates from the Truong Son range, Huong Lap commune, Huong Hoa district, Quang Tri province, Vietnam, flows through the Laos-Vietnam border in Savannakhet province into the Mekong River near Savannakhet city.
A tributary of Se Banghiang is the SePon River, originating from Lao Bao in Vietnam.
-
Menam Mun is 750 km long, flowing into the Mekong River at Khong Chiam District, Ubon Ratchathani City, Thailand.
-
Se Don is a tributary in Champasak province and flows into the Mekong River at Pak Se.
-
Sekong is a secondary tributary, originating from the west of A Luoi district, Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam with the name Xe Asap. Sekong flows by Sekong and Attapeu provinces of Laos to the southern border.
There is also a branch called Se Kaman originating from the Dak P'Lo river in Dak P'Lo commune, Dak Glei district, Kon Tum province, Vietnam. On the Lao side, Se Kaman flows through Dak Cheung border district to Xaysettha district, Attapeu to enter the Sekong river.
To Cambodia, the Sekong is called Tonle Kong. It joins with Tonle San in Savat cave near Stung Treng town to form a short section of 8 km and flow into the Mekong River.
-
Two other critical secondary tributaries originating from the Central Highlands of Vietnam are Tonle San and Tonle Srepok. They join together on Cambodian territory in the Stung Treng area, then enter the Sekong to flow into the Mekong River.
-
Tonle Sap is a river with a large basin that occupies a large part of Cambodia in Central and Northwest, along with the Great Lake, flowing into the Mekong River in Phnom Penh.

The Tonle Sap lake
History
The earliest known civilization is the Malay and Indian culture of the Kingdom of Funan, the Mekong basin in the 1st century. Excavation in Oc Eo region, near present-day Rach Gia city, Kien Giang province, Vietnam, found coins that were different from those of the Roman Empire.
The Funan Kingdom was followed by the Khmer Chenla nation until the 5th century. The Khmer Angkor Empire was the last country influenced by the Indian culture in the region.
The first European to explore the Mekong River was the Portuguese named Antonio de Faria in 1540.
Also, the French had a particular interest in this area in the middle of the 19th century. The first systematic expedition was the expedition of the Mekong River from 1866 to 1868 by the French Ernest Doudart de Lagree and Francis Garnier.
From 1893, the French extended their control over the river, reaching Laos territory, by establishing the Indochina Federation in the first years of the 20th century. It was stopped after the First Indochina War ended and the Americans intervened in the area.
After the Vietnam War, disagreements between Thailand, Vietnam, and China at the time limited the cooperation of the parties in exploiting the potential of this river. However, the parties are now closer together in this regard.
Rare and precious animals
The most important and abundant resource of the Mekong River is water and biodiversity. The biodiversity of the Mekong's fauna and flora is just behind the Amazon basin in South America.
The flow of the Mekong River is plentiful, cultivating vast wetlands and forests, transporting and supplying construction materials, medicines, and food.
Also, it is a habitat for thousands of plants and animals. The Mekong River is one of the largest freshwater fish production areas in the world, with over 1300 types of fish living. The seasonal fluctuating flow regime has provided the environment and food for animals and aquatic species of the basin.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature said scientists were looking for creatures such as Australian fish, catfish, giant stingrays, sharp-toothed freshwater needlefish, large carnivorous carp in the Mekong, etc. These fish can weigh more than 90 kg and are over 1.80 meters long.
Besides, the Mekong also has the rare, precious devil catfish and crystal eyed catfish, not to mention giant barb and giant carp. Fishing tourism services are therefore very developed here.
In particular, there is Irrawaddy dolphin in the Mekong River sections of Cambodia and the Tonle Sap Lake. Perhaps the number of this species are only a few dozen individuals.

Freshwater dolphins in the Mekong River
On August 24, 2012, the Cambodian government set up a 180-km Mekong river dolphin reserve, stretching from Kratie province in the east to the border with Laos. People are still allowed to fish in the reserve, but the government prohibits the use of floating houses, fish rafts, and nets because they threaten the life of the river dolphins.
Several giant freshwater species are listed in the Red Book of Threatened Species of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), including giant Australian fish - the largest freshwater fish of the same family with the barbeled houndshark.
Economy
In a recent announcement (2017), scientists together with the Mekong River Commission (MRC) had many answers about the economic value brought about by the 12th longest river in the world. Accordingly, only the value of fisheries caught from the lower Mekong River had reached 17 billion USD a year.
It has contributed 3% to the GDP of the group of Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, and Thailand. If compared to the total global fishing value of 2015 of 130 billion USD, the Mekong River is accounting for 13%.
Since the beginning of the 90s of the last century, the trend of cooperation, development, and integration has become the mainstream, promoting participation in the Mekong sub-region. Cooperation, economic development, poverty reduction, and environment and water protection are "motivations" to urge countries in the Mekong basin to seek bilateral and multilateral cooperation mechanisms.
In this context, Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) was formed in 1992 under the initiative of the Asian Development Bank (ADB).
The goal of GMS is to promote economic growth, sustainable development, poverty reduction, and improve the lives of people in the Mekong Basin. Therefore, the countries in the region have agreed to cooperate in developing transport, agricultural, energy, and telecommunications infrastructure to facilitate trade, tourism, and human resource training, etc.

Agriculture is very developed in the Mekong River
In particular, cooperation in transport infrastructure development was the priority and has achieved many outstanding results. It focused on three main economic corridors, including the East-West Economic Corridor (EWEC), North-South Economic Corridor (NSEC), and the Southern Economic Corridor (SEC).
In 2007, the GMS adopted the 2006-2015 Mekong Sub-regional Traffic Strategy to revise the planning of sub-regional economic corridors into 9 corridors. From that, it opened routes linking the previous three main corridors and new Western routes linking the Mekong sub-region with India.
Furthermore, water resources on the Mekong River have created great opportunities for countries in the basin of hydroelectricity and commerce. These are also the main economic sectors of the countries in the region. Besides, there are many minerals in the Mekong basin, such as tin, copper, iron ore, natural gas, potassium carbonate, and precious stones.
The proportion of the working-age population (14-64 years old) is quite high here, ranging from 60-70%. The labor force participation rate is also considerably high, opposite to the unemployment rate (2-3%). Some other social indicators, such as the rate of students going to school or the percentage of people who can read and write, are on the rise.
This fact shows that GMS countries are possessing a labor force that is quite abundant, young, and eager to learn, improve their qualifications and knowledge. This is one of the advantages of the sub-regional countries.
In general, GMS cooperation has progressed relatively favorably because countries in GMS have actively promoted collaboration. Currently, the World Bank is considering the possibility of becoming a co-financier with ADB in GMS cooperation.
Travel
River-based tourism along the Mekong is an emerging activity with significant potential for growth. Also, the tourism activities impact on people’s livelihoods.
The Mekong Delta of Vietnam dominates the river’s current cruise tourism scene in passenger numbers and vessels, due in part to the fast and easy road access from Ho Chi Minh City and modern facilities.
Here, travelers will go on small cruises from 1 day (by sampan) to 3 days, from My Tho and Can Tho to floating villages and markets. They will have a chance to enjoy many activities, stay in Mekong riverside resorts, and visit important historical and religious sites. Luxury multi-day delta cruise itineraries will take travelers to/from Phnom Penh.

A day-tour boat in the Mekong Delta
Tonle Sap cruises are popular as an option for traveling between Phnom Penh and Siem Reap. The brief 2 or 3-day itineraries will take them to floating fishing villages and cultural attractions.
The cruise going from Chiang Khong (Thailand) to Houei Xay, Luang Prabang (Laos) has long been the primary transportation connection to/from Chiang Rai. The 2-day itineraries stop at riverside ethnic villages and the notable Pak Ou Cave with an overnight in Pak Beng.
A cruise on the Thai side of the Mekong (Nong Khai-Nakhon Phanom) is offered by Mekong Cruises. Laos's Champassak Province is a growing cruise arena due to river-based attractions. They include the Vat Phou UNESCO heritage site, French colonial infrastructure, activities, and freshwater dolphins.
The Mekong River, with great potential and constant development, is one of the most popular destinations in Asia. There are countless interesting things waiting for you to discover. If you need further information about "Which Vietnam regions does the Mekong River touch?", don’t hesitate to let us know. Like and share the article with others if you find it useful for you. Thank you.